Wireless Communication
5G making inroads in private networks
Traditionally different wireless technologies have been used in communication service provider networks &
enterprise networks. With LTE serious efforts started for deployment in private/enterprise networks, with limited success.
In this blog we share our views on 5G making substantial inroads in private networks!
Private and Public wireless networks provide wireless broadband connectivity. While private wireless networks are owned and operated by an organization for its private use, public wireless networks are owned and operated by telecom service providers to offer wireless services to public at large.
Private Network Technology Choices
Technology choices for building private wires networks include broadband technologies like Wi-Fi or proprietary network technologies like LoRa, Sigfox or cellular technologies like Private LTE, 5G. Factors to choose right technology for private network include spectrum availability; service throughput, latency, security, mobility and quality of service requirements; device, solution total cost of ownership, required manpower competency managing private cellular network. Following table gives a brief summary of
| Feature/Technology |
Wifi |
Private LTE |
Private 5G |
| Throughput |
10Gbps |
1 Gbps |
10 Gbps |
| Mobility |
Fixed / Nomadic |
Full Mobility |
Full Mobility |
| Latency |
~100ms |
~40ms |
~1ms |
| Quality of Service (QoS) |
Best Effort |
Multiple QoS Priority, Pre-emption |
Multiple QoS Priority, Pre-emption |
| Security |
Limited built in security |
Security built in solution |
Security built in solution |
| Density |
~10K / square KM |
~100k / square KM |
~1 m / square KM |
| Spectrum |
Unlicensed 2.4/5 GHz, 1/6 GHz (Emerging) |
Licensed and Unlicensed band |
Licensed and Unlicensed band |
| Device Cost |
Very Low |
Low |
High |
| Solution TCO |
Low |
Med |
Med |
| Equipment Availability |
High |
Stable |
Emerging |
| Enterprise Competency |
High |
Low |
Low |
| Target Use Cases |
Enterprise IT |
Mines,Mission Critical, Smart Factories, Smart Campuses |
Mines, Mission Critical, Smart Factories, Smart Campuses |
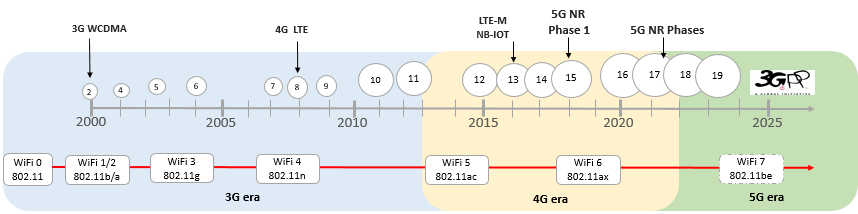
Both Wifi and Cellular technologies (3G, 4G, and 5G) have evolved over last 2 decades. Following diagram shows evolution of both Wifi and cellular technologies over last 20 years.
Following table gives a bird eye view of evolution of WiFi standards and incorporation of various new radio features like improved modulation, advanced signal processing and multiple antenna usage that ensured WiFi technologies remain at part with evolving cellular technologies
| Feature/Version |
Wifi 1 |
Wifi 2 |
Wifi 3 |
Wifi 4 |
Wifi 5 |
Wifi 6 |
Wifi 7 |
| Standard |
802.11b |
802.11a |
802.11g |
802.11n |
802.11ac |
802.11ax |
802.11be |
| Year |
1999 |
1999 |
2003 |
2009 |
2013 |
2020 |
2024* |
| Band (GHz) |
2.4 |
5 |
2.4 |
2.4/5 |
5 |
2.4/5/6 |
2.4/5/6 |
| Bandwidth (MHz) |
22 |
20 |
20 |
20-40 |
20-160 |
20-160 |
20-320 |
| Throughput |
11 mbps |
54 mbps |
54 mbps |
600 mbps |
6.8 gbps |
6.9 gbps |
46.1 gbps |
| Modulation |
DSSS/CCK |
OFDM |
|
16/64 QAM |
64/256 QAM |
1024 QAM, OFDMA |
4096 QAM |
| Radio Features |
|
|
|
MIMO, Beam Forming |
multi-user MIMO, 4 x 4 MIMO |
Dual band, BSS Coloring |
Multi band coordination |
Private Network Use Cases
There are a number of industry verticals that make excellent candidates for the use of private wireless networks that include energy and utilities, airports, ports and train stations, warehouses and other retail premises, healthcare, smart factories and education institutes, to name a few.
- Smart Factories:–A smart factory is a manufacturing facility that uses digitization and advanced technologies to improve efficiency and productivity. In a smart factory all equipment are interconnected allowing them to communicate and share data in real time. Smart Factories require communication network with low latency, high through and security to enable them to deploy advanced robotics like automated guided vehicles (AGV) and Industrial IOT enabled machines. Germany has seen private LTE/ 5G networks with local spectrum getting deployed in automotive manufacturing. It is expected to be replicated other geographies and other industry verticals.
- Mines:– Mines typically have tough work environment being remote, hazardous, inaccessible, rough terrain and operations requiring mission critical characteristics. Digital solutions are transforming wide variety of business applications including improving safety, increasing production, lowering costs, and optimising mine plans. Private LTE and 5G networks provide reliable connectivity for drilling machines, rugged handhelds, and other equipment, even if this equipment is underground or in a remote location.
- Warehouses:– Warehousing and Logistics industry have gone through cycle of automation lead by increase in E-Commerce. Warehouse operators and online retailers are deploying robotic product picking, product tracking, and other Industrial IOT warehouse applications. Private Networks help them deploy these technologies without worrying about dead spots in their warehouse or spending a lot on network maintenance.
- Smart Campuses:– Smart Campus links devices, applications, and people to enable new experiences and improving operational efficiency. As more devices like sensors, cameras, lighting, vehicles, ID cards are added to networks; campus services are managed more efficiently and automatically. Private LTE or 5G networks enables smart campus services like smart ID cards, smart payments, finding free parking or bike share, real time bus information, smart locks or access control for different locations, providing ubiquitous indoor and outdoor wireless coverage by providing personal student networks.
- Airports:– Some airports are so large and diverse that they actually resemble cities. They have hundred of companies as tenants, thousands of employees, ten thousands of passengers and visitors, airport internal as well as visitor vehicles, variety of equipment like aircrafts, cargo vehicles , security cameras and other IOT devices. Private LTE or 5G networks enables use cases like critical communication for airport operations, Baggage tracking and cargo management, Passenger services like broader control, security control and information disbursements, aircraft and airline equipment connectivity etc.
As per recent GSA (Global Mobile Supplier Association) report on private mobile networks deployments.
- Number of customers deploying private mobile networks reached ~1100 globally.
- Number of countries having private mobile networks reached 74
- Manufacturing, Education and Mining largest sectors for private mobile networks deployment
There are ~ 1 million factories, ~3000 Mines and ~1000 ports in world just to give hint on size of opportunity for private networks and potential impact they can bring.
Choices of Spectrum for Private Networks
Spectrum is key factor influencing the uptake of wireless solutions, typically reliable wireless connectivity demands licensed and dedicated spectrum for service. Spectrum is owned by government and is licensed to enterprises for use within a geographical area usually for 10-20 years. Telecom Service Providers (TSP) get licensed spectrum to deploy public wireless network across country. Around the world, regulators are exploring various strategies to spectrum management that makes room for private network allocations. Following are some options that regulators are considering and trying out in different countries to support private networks.
- Local/Regional licensed spectrum - Enterprises requiring spectrum for their premises are provided local or regional licenses allowing enterprises or subnational operators to operate their own private/local 5G network using localised spectrum license for their premises.
- Spectrum leasing - allowing businesses wanting to operate their own 5G infrastructure to lease spectrum on a localised basis from public network operators holding national 5G spectrum licences
- Shared spectrum - allowing businesses wanting to operate their own 5G infrastructure to apply for licences in a shared spectrum band, which will need to be coordinated with other users in the same band.
- MNO Network Slicing - allowing TSP to offer dedicated solution to enterprises using their spectrum and its ecosystem of solutions.
As per recent GSA report, top five counties for private networks are the United States, Germany, China, the UK and Japan, Finland and France. Dedicated spectrum is allocated in most of these markets. GSA expects the correlation between the number of private networks and countries with dedicated spectrum to continue in the coming months.
- Germany has set aside 100 MHz spectrum in 3. 3.4-3.8 GHz band for local licenses. Many companies are awarded this license and using it primarily for automotive manufacturing use case.
- U.K. has allowed localized and shared spectrum licenses in 3.8-4.2 GHz band. More than 1000 licenses have been issued so far to different enterprises in wide ranging applications.
- France opened up frequencies in 3.8GHz-4.0GHz, 2.6GHz and 26GHz bands to support private networks in addition to network slices from TSP. Progress in France has been slow and as of now less than 20 licenses have been awarded.
- Sweden auctioned spectrum in 3.7-3.8 GHz band for local and regional licenses to support private networks.
- Finland has set aside spectrum in 2.3-2.4 GHz band for private networks on a first come first served basis.
CBRS suitability for Private Networks
CBRS (Citizens Broadband Radio Service) is 150 MHz of spectrum in 3.5-3.7 GHz band in United States that has been made available by the FCC for private wireless networks. The three tiers of users for this spectrum are:
- Incumbent, such as the United States Navy and fixed satellite
- Priority Access License (PAL), enterprises that pay to get license of the spectrum
- General Authorized Access (GAA), enterprises that utilize spectrum unlicensed
CBRS auction took place in July 2020 for seven PALs per county, totalling 22,631 PALs nationwide. Auction resulted in large communication giants such as Dish Network, Verizon, and Charter Communications winning regional slots and small cable operators and technology companies getting county specific licenses.
Though the FCC auctioned some CBRS licenses, called Priority Access Licenses (PALs), companies can still use General Authorized Access (GAA) CBRS spectrum without obtaining a license, sharing this spectrum with PAL license owners (who have priority access to the spectrum) and other GAA users. This allows both PAL license owners and GAA users to build and operate private networks in the United States using the CBRS 3.5 GHz band of wireless spectrum With all these developments it is clear that number of private 5G networks deployments are set to explode in coming years. A new set of ecosystem players offering solutions and services for this segment are coming up at rapid pace.